Ancient Egyptian food was influenced by the fertile Nile, offering a varied diet based on geography, social status, and religious customs. Bread and beer were staples for all, while the wealthy enjoyed meat, poultry, and spices. Vegetables like onions and garlic, and fruits such as dates and figs, were common. Preservation techniques like drying, salting, and fermenting were used, with honey as the primary sweetener. Food played a role in religious rituals, and preparation methods included stewing, baking, grilling, and boiling. The use of spices, oils, and grains by the ancient Egyptians has left a lasting impact on culinary practices.


Ancient Egyptian food included lots of different dishes, as the Egyptians had a great taste when it came to their cuisine. No one has left Hungary in Ancient Egypt; they enjoyed a great variety of foods not much different from what we consume today.
The ancient Egyptian civilization had access to better food due to their rich soil and the Nile River, which provided irrigation for the crops and water for the livestock. The ancient Egyptians were able to cultivate the art of cooking as they changed how ancient people looked at food by creating amazing recipes.
The ancient Egyptian society main food was bread and beer, often accompanied by fruits, vegetables, and fish, eaten by the poor, while meat and poultry were eaten by the rich. The ancient world was not good for health, as the food was less nutritious, but in Egypt, it was a different story, as the food led to the overall prosperity and fertility for thousands of years.

Many carvings and images can be found on temple and tomb walls showing ancient Egyptian food from Egypt old kingdom (2700–2200 B.C.E) and Egypt new kingdom (1570–1070 B.C.E). Most depictions were in the afternoon, and men and women were separated in the images unless they were married. The seating positions varied according to social status, with those in the higher status sitting on chairs while the middle class sat on stools and the lowest class sat on the raw floor.
Before the food was passed, basins were provided with perfume cones to spread pleasant smells. The dishes consisted of stews served with great amounts of bread, fresh vegetables, and fruit, and for dessert, there were cakes baked with dates and flavored with honey.

The ancient Egyptian diet was rich in grains and vegetables, which was nutritionally adequate and sustained a large population. The Ancient Egyptian cuisine was largely shaped by the geography, the environment, and the Nile’s cycles, and the Egyptians used every resource available to ensure food security. The fertile land around the Nile River provided a wide variety of food, and the diet varied based on social status. Here is a comprehensive list of what Ancient Egyptians ate:
Bread: Made from emmer wheat or barley, bread was a primary component of the Egyptian diet. It was often thick and coarse due to the use of stone-ground flour, which introduced small particles of sand into the bread which causing tooth wear, which can be seen in the mummies.
Beer: Made from fermented barley, beer was a staple drink in Egypt and consumed by all classes. It was thick, more like a porridge than modern beer, and flavored with herbs or fruits. Different types (red and black beer) were categorized by alcohol content.
Wines were also made from fruits like dates, figs, and pomegranates. Wine was made in small quantities for the elite, with some imported from Greece and Mesopotamia.
Discover the lives and foods of the ancient Egyptian people
Read More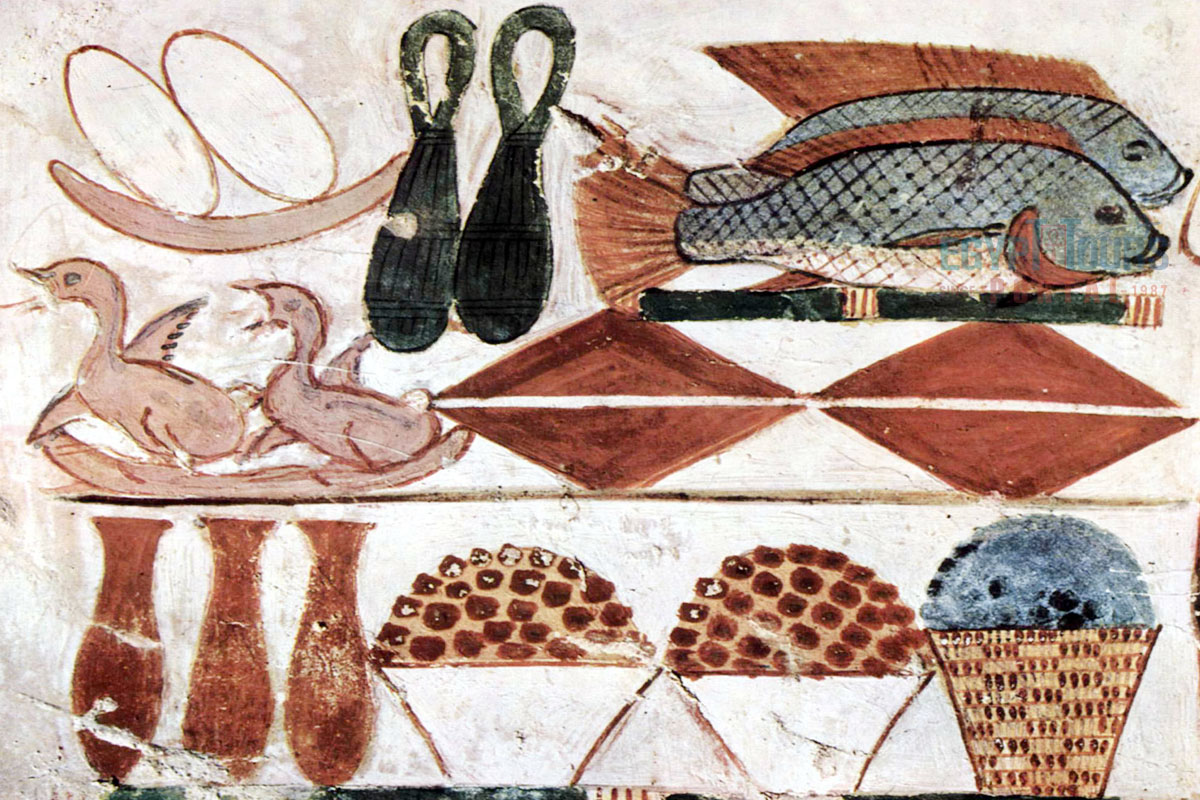
The main source of food for the Ancient Egyptians came from the fertile lands of the Nile River Valley, which provided ample crops for consumption. Key sources included:
Agriculture: The Nile's annual flooding deposited rich silt on the banks, making the land fertile for growing wheat, barley, lentils, vegetables, and fruits. The ancient Egyptians were skilled farmers who grew a wide variety of crops.
Fishing: The Nile River and the Mediterranean Sea were rich sources of fish. Fishing was an important food source, especially for commoners.
Livestock Farming: Egyptians raised cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs, but meat was more of a luxury for the wealthy. Poultry, such as ducks and geese, was more widely available.
Trade: Egypt traded with neighboring regions for goods such as spices, exotic fruits, and oils, allowing the wealthy to access a broader array of foods.

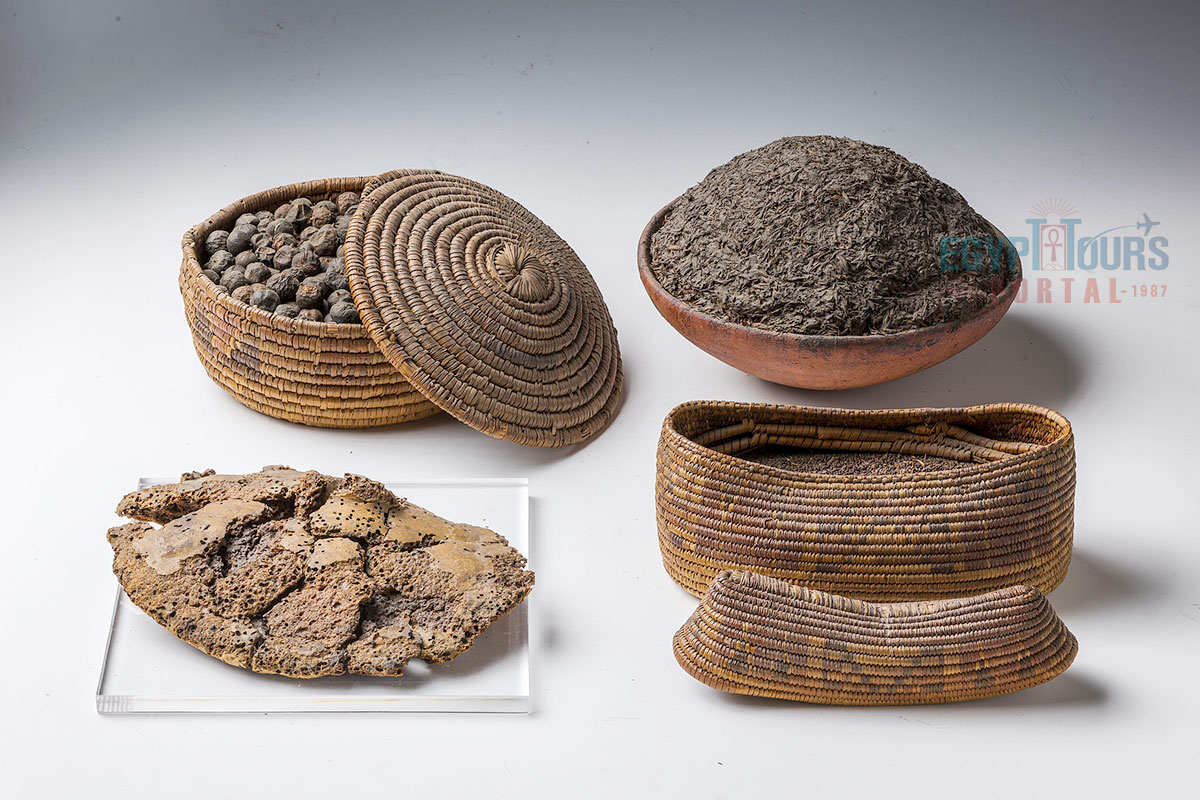
Food preparation and cooking in ancient Egypt were a complex process involving various methods such as stewing, boiling, baking, grilling, frying, and roasting. Archaeological findings, including records and depictions in ancient Egyptian tombs and on papyrus scrolls, reveal that the Egyptians used herbs and spices to enhance flavor, although these spices were expensive imports, making them available only to the wealthy. To preserve their food, Egyptians used methods like salting meat and drying fruits, such as dates and raisins, for long-term storage.
The primary sweetener in ancient Egyptian cuisine was honey, which was harvested from wild or domesticated bees kept in pottery hives and was also a costly commodity. Cooking oils made from lettuce, safflower, beans, sesame, balanitis, and olive were commonly used, along with animal fats, which were all stored in jars for preservation.
Bread and beer, both vital staples in Egyptian diets, were often made together, as the yeast used for bread also served as a fermenting agent for beer. These staples were typically produced in dedicated bakeries, though many households made them at home, selling any surplus in the market.

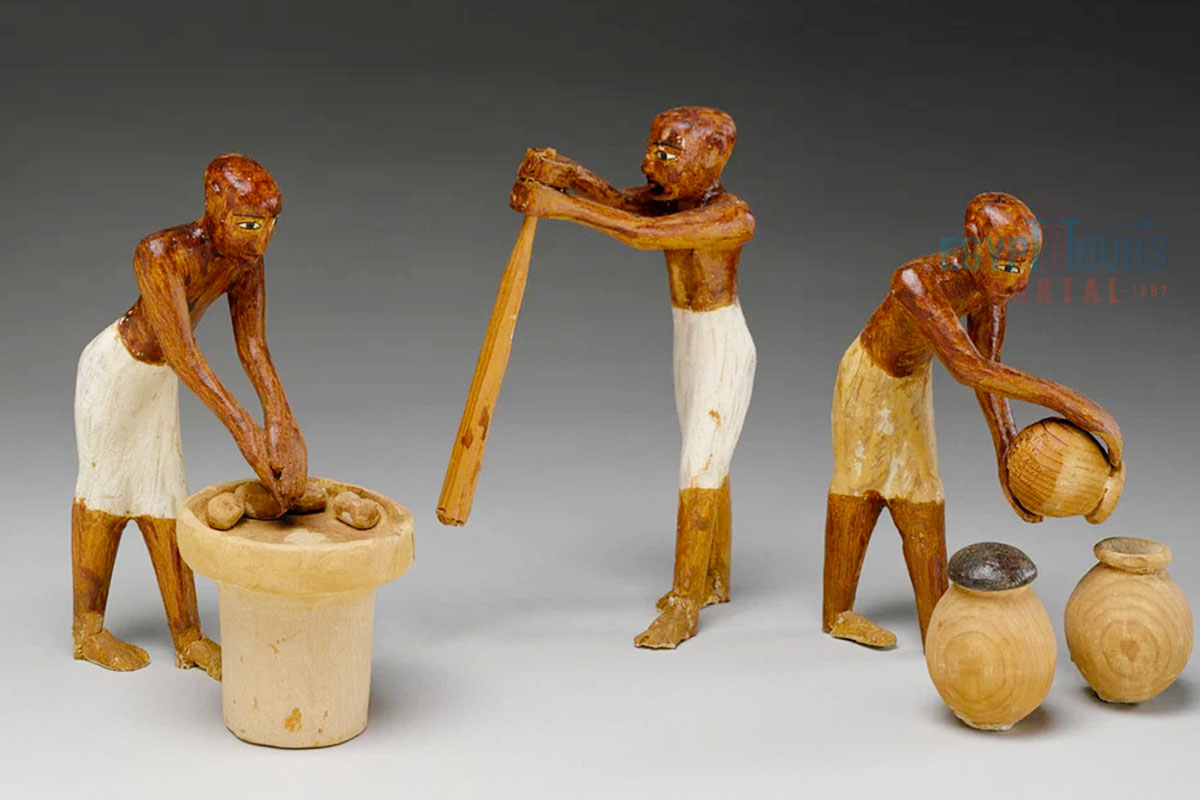
Over the years, the ancient Egyptians were able to use their intelligence and creativity to create several essential recipes that harnessed the crops of their blessed environment. Here are some typical ancient Egyptian food recipes used during the golden times of the ancient Egyptian civilization:
Bread: Bread was made by mixing flour from emmer wheat or barley with water. The dough was sometimes enriched with dates, honey, or herbs. It was baked in clay ovens or on hot stones. Ancient bread was often dense and gritty due to the coarse flour used.
Beer: To make beer, barley was first sprouted, dried, and ground into a mash. This mash was mixed with water, fermented, and strained, resulting in a thick, nutritious beverage. Beer was often flavored with dates or herbs.
Lentil Stew: Lentils were boiled with onions, garlic, and leeks, seasoned with salt and herbs. Sometimes, oil or fat from animals was added to give the stew richness. It was a popular and simple dish.
Fish Preparation: Fish was cleaned, salted, and either dried or smoked for preservation. Fresh fish was grilled or boiled and served with bread or vegetables.
Duck or Goose Roasted with Figs: Wealthier Egyptians enjoyed roasted meats, especially ducks or geese. These were sometimes stuffed with figs or dates for added flavor, then roasted over an open flame or in an oven.
Some of the most common recipes in ancient Egypt included:
Ingredients:
Preparation:
Ingredients:
Preparation:
Ingredients:
Preparation:
Ingredients:
Preparation:
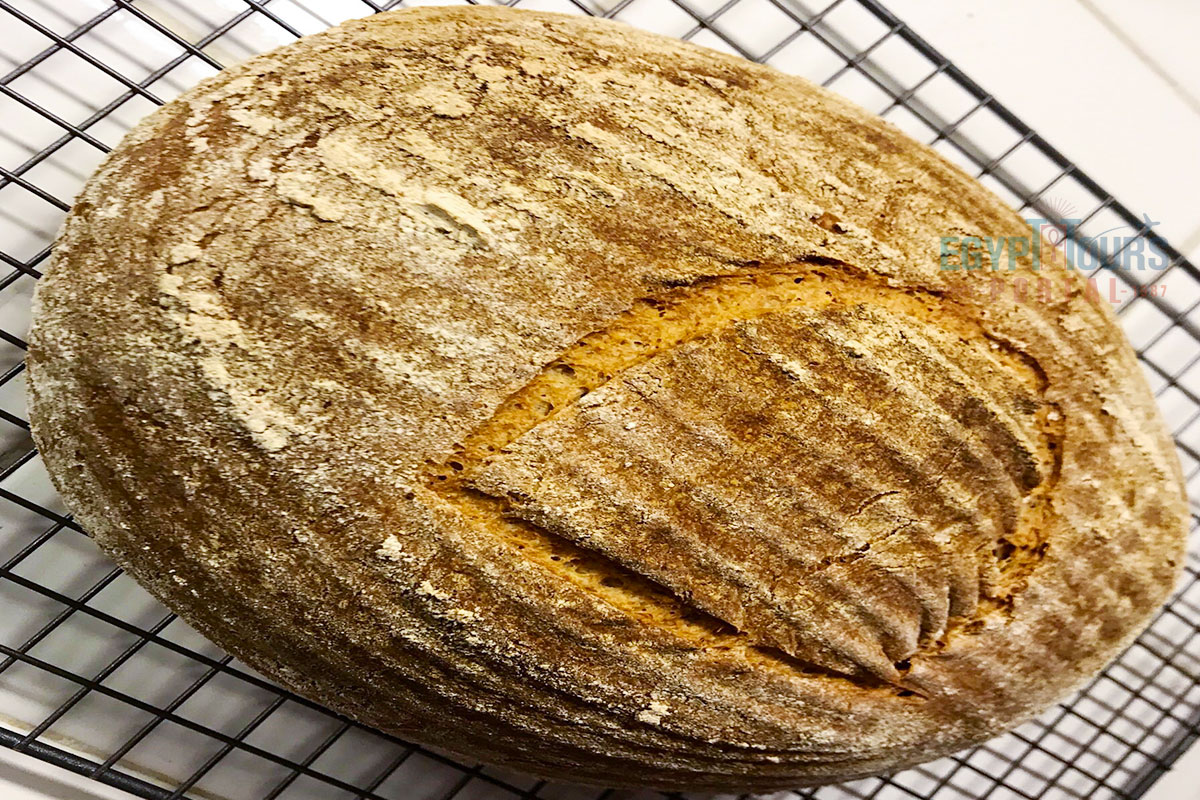

The staple of ancient Egyptian cuisine was bread, which was eaten by both the rich and the poor. It was consumed daily and was made from wheat or barley. Making bread was a strenuous task were the grains first grounded into the floor by women through a grinding mill to form a flour. The sand was added into the grinder to speed up the process, which means the bread has sand in it that was the cause of many dental problems, like tooth decay, as evident in the teeth of various mummies.
When mixing the flour with water and yeast, the dough would be formed, which would then be placed in a clay mold before being cooked in a stone oven. There were fine desserts, bread, and cakes made from high-grade flour. The bread came in different sizes and shapes like human figures, fish, and many animals; they were also seasoned with coriander seeds and dates.
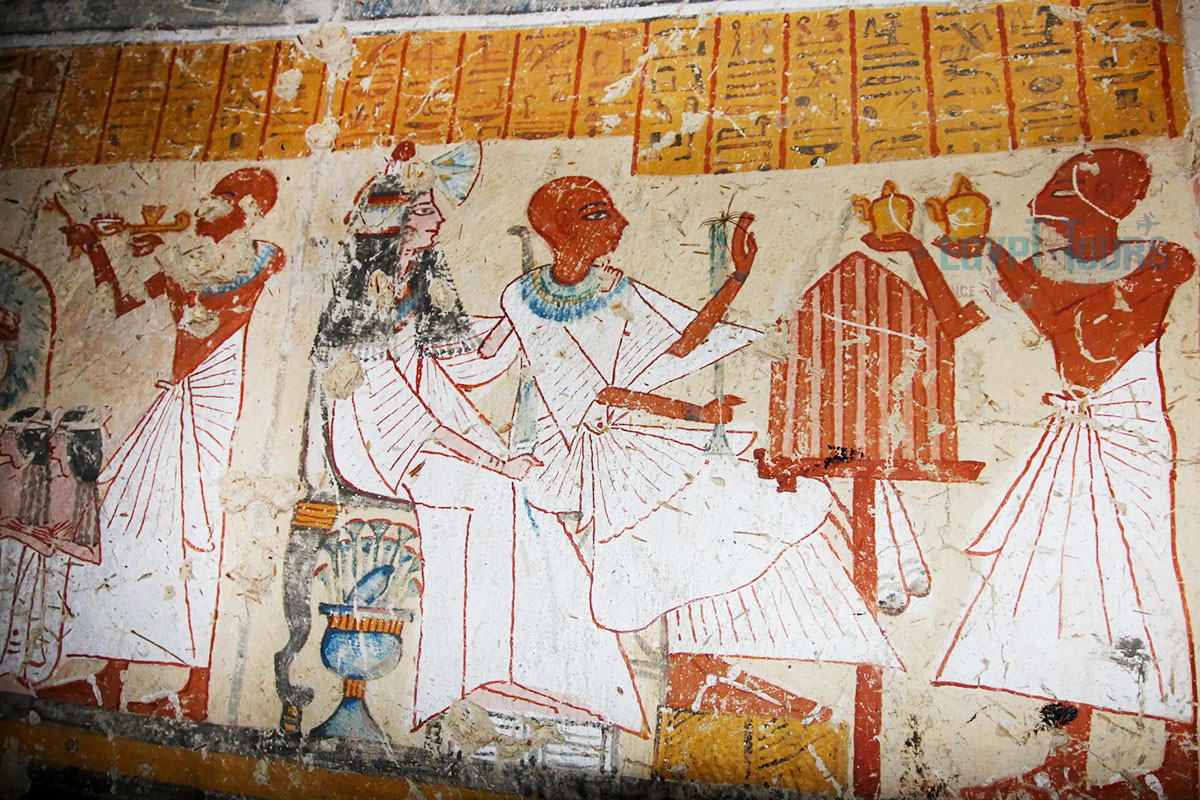

Beer was the most common drink in Ancient Egypt, the cornerstone of ancient Egyptian beverages. It was called "Beer Bread was an important part of the Egyptian diet and was even used as a currency. Most of the ancient Egyptians did not drink water directly from the Nile, as they observed that people got sick after drinking it, so they drank beer instead.
The Ancient Egyptians made beer by half-cooking barley, then soaking it in water and leaving it to set. It was highly nutritious food containing high protein, minerals, and vitamins. It was the same thickness as a milkshake and contained a low level of alcoholic content. The ancient Egyptians also made white and red wine from grapes, which were combined with spices and honey. They made many non-alcoholic drinks from fruits like dates.
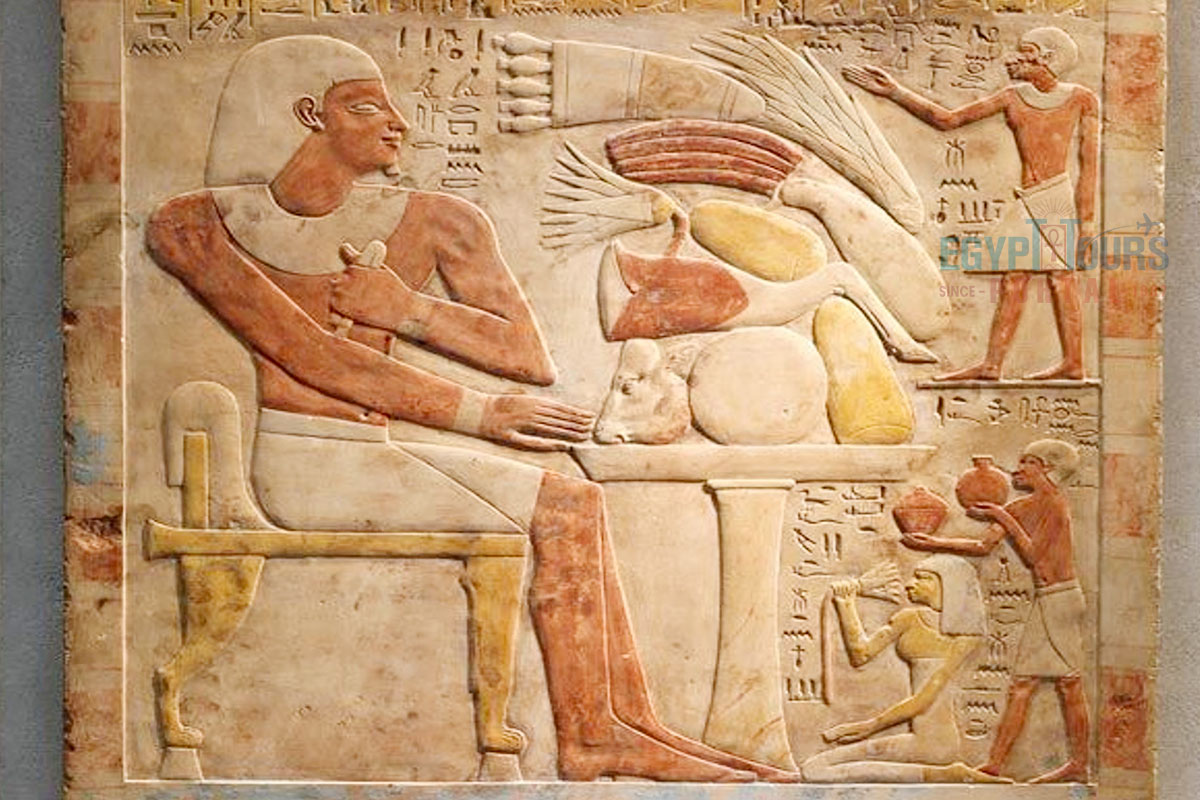
Despite the fact that the Nile was not the main source of hydration, it was the main reason for the land's fertile nature and the variety of ancient Egyptian food due to its annual flooding, which allowed the plantation of various crops of fruits and vegetables.
The most common vegetables were green onions and garlic, which were used for medical purposes, plus leek, cucumber, lentils, lettuce, celery, beans, peas, lentils, radish, and turnip, plus the papyrus, which was used to create paper, was eaten raw, boiled, and even roasted. The most common fruit was dates, but they also consumed fruits like figs, grapes, melons, apples, and pomegranates.
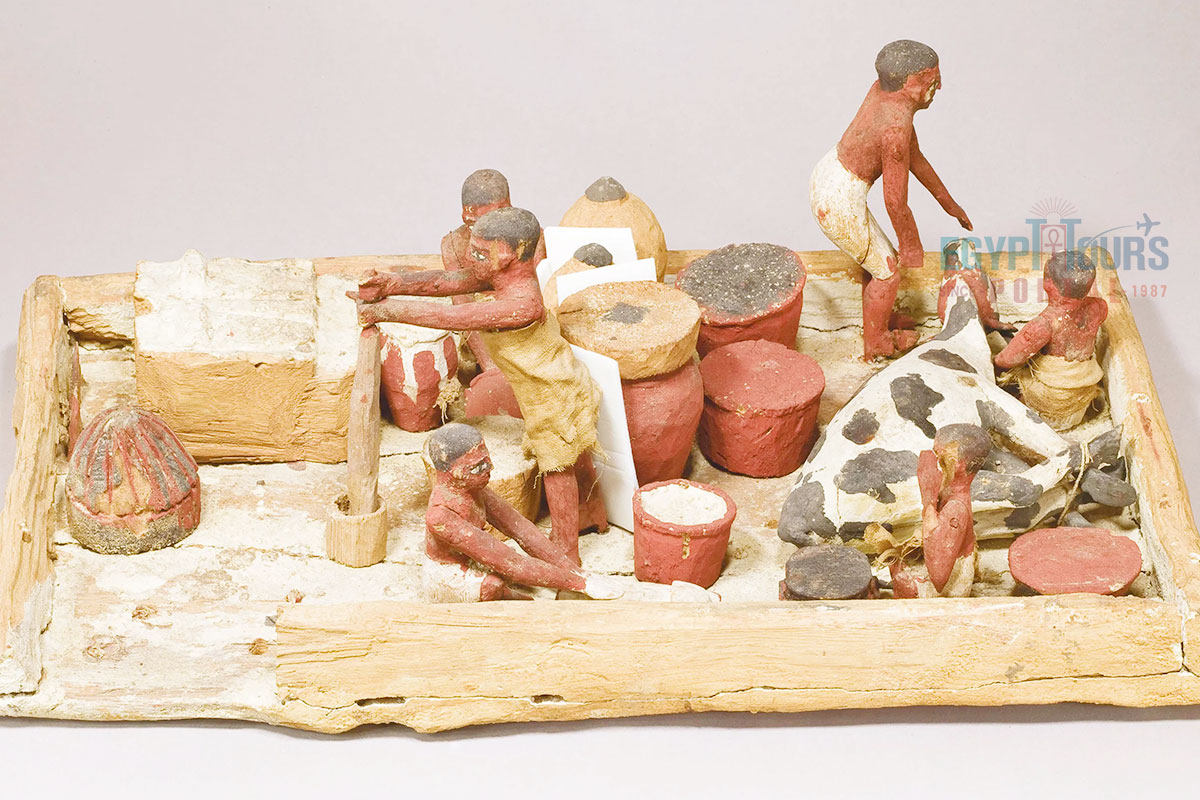

Meat was a valuable but not always readily available source of protein. While fish and poultry were more common and accessible to a wider range of people, red meat like beef was expensive and typically consumed by the ancient Egyptian nobles, the wealthy, or during special occasions. Pigs, though considered unclean by ancient Egyptian priests, were commonly consumed by the less affluent, and various wild animals such as wild boar, gazelle, antelope, hippopotamus, and crocodile were hunted, often reserved for the elite.
Cattle, particularly prized for their red meat, were highly valued, with the left foreleg being considered especially valuable. Sheep and goats were also sources of red meat, primarily for those who could afford them. Fish, a staple protein, was often preserved through drying or salting. Meat preservation techniques, including salting and drying, were widely used to extend shelf life, particularly for trade or long-distance travel.
Other preservation methods, such as smoking and curing with fat, beer, or honey, were also utilized. Meat preparation methods included boiling, roasting, and grilling, while sausages, like the spicy sogouq, and other dishes such as trotters soup were also popular in ancient Egyptian cuisine.
Discover the incredible animals and meat sources of the ancient Egyptian civilization
Read MoreEverything in Egypt feels like heaven, so don't miss the chance to explore the beauty and wonder of this holy country with a magical Nile river cruise and an Egypt vacation to the great cities of Cairo, Luxor, Alexandria, Hurghada, and Aswan.
Private 4 Days Cairo Tour Packages for New Zealander Travelers 4 days Cairo Egypt To...
Tour Location: Cairo – Giza...
5 Days Cairo and Alexandria Tour Package For New Zealander Travelers 5 days Cairo an...
Tour Location: Cairo/Giza/Alexandria...
6 Days Cairo, Luxor & Aswan Tour Package For New Zealander Travelers 6 days Cair...
Tour Location: Cairo/Giza/Aswan/Luxor...
Amazing 7 Days Cairo and Hurghada Holiday for New Zealander Travelers 7 Days Cairo &...
Tour Location: Cairo – Giza – Hurgh...
Food preparation in Ancient Egypt was mainly a household activity that was performed by wives and female family members, who were primarily responsible for cooking and preparing food. In wealthier households, servants often handled this work. For religious ceremonies or offerings to gods, priests or temple staff prepared the sacred meals. Professional cooks and bakers in royal households managed food preparation for the Pharaoh and nobility, with specialized chefs for bread, meats, and other delicacies.
Ancient Egyptians stored food in clay jars, baskets, and granaries. These storage vessels were often sealed with clay or mud to keep food fresh and protect it from pests like insects and rodents. Grain was the staple of the Egyptian diet which was stored in large silos or granaries, typically near temples, homes, or farms.
These storage systems helped Egyptians manage their harvests and maintain a steady food supply, especially during the annual flooding of the Nile, which could affect food availability.
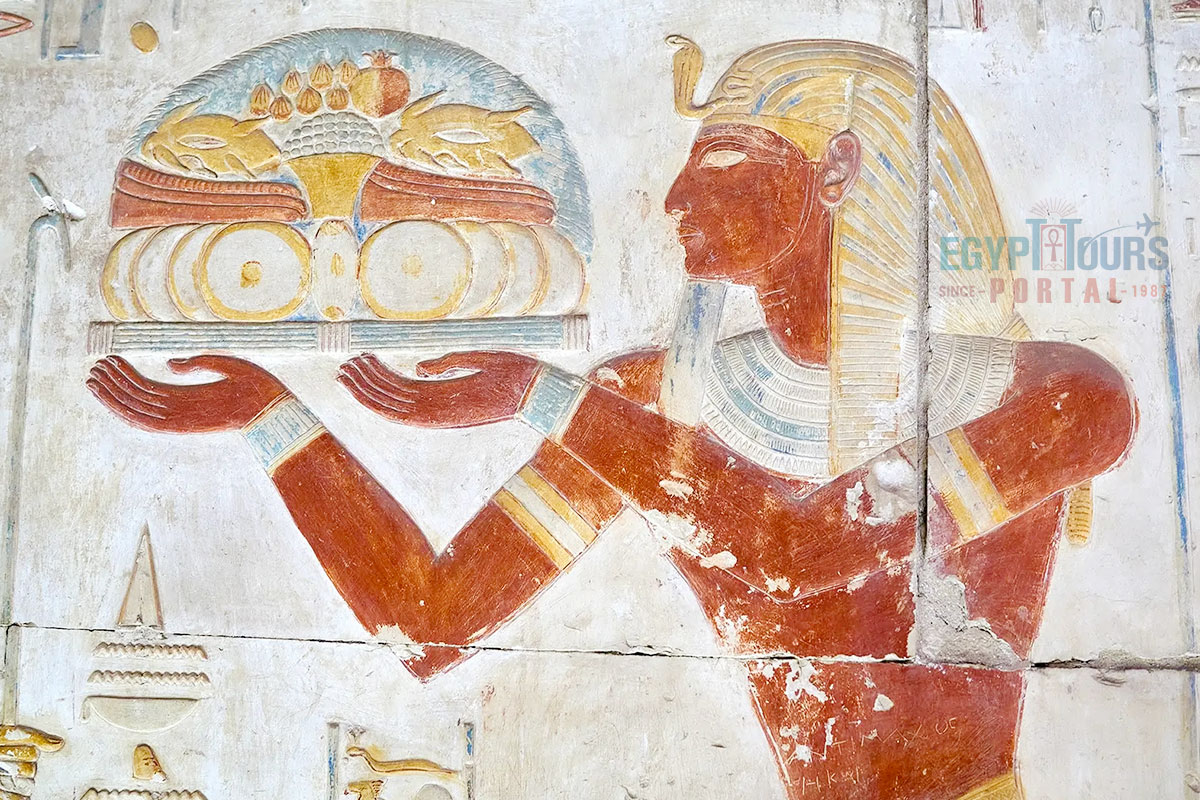
Egyptian priests had very strict diets as part of their religious obligations. They primarily consumed clean and pure foods that were ritually prepared. Staples included bread, vegetables, fruits, fish, and occasionally meat. Priests avoided certain foods like fish on religious grounds, as some types were considered impure. Offerings made to the gods often included bread, beer, wine, and fruits, and priests would consume a portion of these offerings after rituals.
Pharaohs enjoyed a rich and varied diet that reflected their wealth and status. Their meals included fine breads, honey, fruits such as figs and dates, various vegetables, and meats like beef, lamb, and poultry. They also consumed fish, and the finest wines and beers were served at royal banquets.
Pharaohs had access to exotic foods that were not commonly available to ordinary Egyptians, such as rare spices or imported delicacies from neighboring regions. They dined in luxury, often with meals carefully prepared by royal chefs.
Farmers in Ancient Egypt typically kept a portion of their harvest for personal consumption and used the rest to pay taxes or trade. The central administration, including temples and the Pharaoh’s granaries, collected much of the surplus food. Farmers stored grains like wheat and barley in their granaries, often located near their homes or fields, but large portions were allocated to the state as a form of tribute.
The food distribution system ensured that the farmers had enough for their households while supporting the needs of the kingdom and the gods. Their saved portion would often be traded for meats, fish, fruits, and vegetables.
Ancient Egyptian food was simpler and largely plant-based compared to modern diets. Bread, made from emmer wheat or barley, and beer were the staple foods, while fruits, vegetables, legumes, and fish were common. Meat, though eaten, was less frequent for commoners and reserved for special occasions.
Today’s food includes a wider variety of ingredients, modern farming methods, and technological preservation methods that allow for the availability of diverse and processed foods. Ancient Egyptian cuisine lacked processed sugars, refined grains, and modern spices, relying more on local ingredients like honey for sweetening and herbs for flavor.
The Egyptians were keenly aware of food preservation techniques to prevent food waste. Due to the hot and arid climate of Egypt, food spoiled relatively quickly if not properly preserved. To extend the shelf life, Ancient Egyptians developed methods like drying, salting, and fermenting.
Grains and dried foods, such as dates and legumes, could last for long periods when stored properly in sealed containers or granaries. Meat and fish were often salted or dried to prevent spoilage. Fresh produce and cooked food would spoil within a few days in the absence of refrigeration, which did not exist at the time.
The entire country of Egypt deserve to be explored with its every heavenly detail but there are places that must be seen before any other such as the breathtaking Hurghada's red sea, The wonders of Cairo the pyramids of Giza, the great sphinx, the Egyptian Museum, Khan El Khalili Bazaar, the wonders of Luxor like Valley of the Kings, Karnak & Hatshepsut temple and the wonders of Aswan such as Abu Simbel temples, Philea temple, Unfinished obelisk and The Wonders of Alexandria like Qaitbat Citadel, Pompey's Pillar and Alexandria Library. Read more about the best places to visit in Egypt.
If you want to apply for a Visa On Arrival that lasts for 30 days then you should be one of the eligible countries, have a valid passport with at least 6 months remaining and pay 25$ USD in cash, as for the E-Visa for 30 day you should have a valid passport for at least 8 months, complete the online application, pay the e-visa fee then print the e-visa to later be presented to the airport border guard. You could also be one of the lucky ones who can obtain a free visa for 90 days. Read more about Egypt travel visa.
Egypt has a variety of delicious cuisines but we recommend “Ful & Ta’meya (Fava Beans and Falafel)”, Mulukhiya, “Koshary”, a traditional Egyptian pasta dish, and Kebab & Kofta, the Egyptian traditional meat dish.
The best time to travel to Egypt is during the winter from September to April as the climate becomes a little tropical accompanied by a magical atmosphere of warm weather with a winter breeze. You will be notified in the week of your trip if the Climate is unsafe and if any changes have been made.
You should pack everything you could ever need in a small bag so you could move easily between your destinations.
We have been creating the finest vacations for more than 20 years around the most majestic destinations in Egypt. Our staff consists of the best operators, guides and drivers who dedicate all of their time & effort to make you have the perfect vacation. All of our tours are customized by Travel, Financial & Time consultants to fit your every possible need during your vacation. It doesn't go without saying that your safety and comfort are our main priority and all of our resources will be directed to provide the finest atmosphere until you return home.
You will feel safe in Egypt as the current atmosphere of the country is quite peaceful after the government took powerful measures like restructuring the entire tourist police to include all the important and tourist attractions in Egypt. Read more about is it safe to travel to Egypt.
Wear whatever feels right and comfortable. It is advised to wear something light and comfortable footwear like a closed-toe shoe to sustain the terrain of Egypt. Put on sun block during your time in Egypt in the summer to protect yourself from the sun.
The best activity is by far boarding a Nile Cruise between Luxor and Aswan or Vise Versa. Witness the beauty of Egypt from a hot balloon or a plane and try all the delicious Egyptian cuisines and drinks plus shopping in old Cairo. Explore the allure and wonders of the red sea in the magical city resorts of Egypt like Hurghada and many more by diving and snorkeling in the marine life or Hurghada. Behold the mesmerizing western desert by a safari trip under the heavenly Egyptian skies.
There are a lot of public holidays in Egypt too many to count either religious or nation, the most important festivals are the holy month of Ramadan which ends with Eid Al Fitr, Christmas and new years eve. Read more about festivals & publich holidays in Egypt.
Egypt is considered to be one of the most liberal Islamic countries but it has become a little bit conservative in the last couple of decades so it is advised to avoid showing your chest, shoulders or legs below the knees.
Arabic is the official language and Most Egyptians, who live in the cities, speak or understand English or at least some English words or phrases. Fewer Egyptians can speak French, Italian, Spanish, and German. Professional tour guides, who work in the tourism sector, are equipped to handle visitors who cannot speak Arabic and they will speak enough English and other languages to fulfill the needs of all our clients.
The fastest way is a car, of course, a taxi. If you are in Cairo ride a white taxi to move faster or you could board the fastest way of transportation in Egypt metro if the roads are in rush hour.
The temperature in Egypt ranges from 37c to 14 c. Summer in Egypt is somehow hot but sometimes it becomes cold at night and winter is cool and mild. The average of low temperatures vary from 9.5 °C in the wintertime to 23 °C in the summertime and the average high temperatures vary from 17 °C in the wintertime to 32 °C in the summertime. The temperature is moderate all along the coasts.
It is the home of everything a traveler might be looking for from amazing historical sites dating to more than 4000 years to enchanting city resorts & beaches. You will live the vacation you deserve as Egypt has everything you could possibly imagine.









